What is DMARC: Using a DMARC Record to Protect Your Domain
DMARC Explained

Implement a DMARC record to create a safe environment for both your company and your audience. As the most effective email validation system, DMARC records protect your domain from business email compromise.
According to Verizon, 94% of all malware comes from email. Phishing attacks consist of 80% of all incidents. About $17,700 is lost every minute on average due to phishing attacks.
In this article, we cover:
What is DMARC?
DMARC or “Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance” is an email authentication, policy, and reporting protocol. In simpler terms, DMARC allows you to improve email security by:
- Preventing unauthorized use of your email domain
- Protecting your email recipients from phishing, spoofing, and other fraudulent email scams that may use your brand’s reputation to trick users into opening a malicious email.
Think of DMARC as a security guard for your email server; it monitors what comes in and out.
Why is DMARC Important?
DMARC authentication protects domain owners from spammers by sending DMARC reports that alert the sender about unauthorized IP addresses and email traffic.
One of the reasons why email spoofing and phishing rates are still high is because, unfortunately, many companies do not understand how important a DMARC policy is for your brand and customer security.
It is crucial to understand that anyone can be a target of cybercrime. Cybercriminals do not just target the biggest businesses. What is happening without DMARC:
So if you think your business is secured without DMARC, read the next section.
Risks of not Having a DMARC Record:
- Recipient mail servers cannot identify a company’s legitimate email message from a fake one
- A receiving mail server won’t have any instructions on what to do with an email message that fails DMARC authentication (pass, quarantine, or reject)
- A sending domain owner is unaware of any unauthorized activity on their domain
All these risks can lead to billions of dollars in company losses. Cybercriminals take advantage of the lack of email security to steal passwords, bank account information, credit cards, identities, and commit CEO fraud.
Get an in-depth understanding of what it means to be DMARC compliant including its implementation and analysis
How Does DMARC Work?
DMARC works alongside SPF and DKIM. In order to pass DMARC email authentication, you have to make sure that SPF and DKIM work correctly. Together, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC create a perfect authentication trio to secure your domain and your clients.
After you deploy DMARC, every email you send has to undergo these steps:
- Receiving mail servers complete an SPF and DKIM alignment to achieve DMARC domain alignment.
- If the check is complete with no problems, the recipient mail server references your DMARC record policy in your DNS record to determine what to do with your email: Pass it, Quarantine it and send it to the spam folder, or Reject it completely.
- After deciding what to do with your email, DMARC sends you a report about what actions were taken towards this particular email, as well as all other emails sent from your domain.
Additionally, you may want to use third-party tools like a DMARC report analyzer to make your report analysis and storing process easier.
What is a DMARC Record?
A DMARC record helps protect email senders from spoofing and phishing attacks. You have to use a DMARC record to configure your DMARC policy.
DMARC is one of the easiest authentication methods to implement for your email channel. All you need to do is add a TXT record with your DMARC policy to your domain’s DNS record and you are ready to start monitoring your DMARC reports!
Now that you’ve implemented DMARC, created policy settings, and installed a DNS TXT record, you will start receiving domain-based message authentication reporting (DMARC reporting).
How Does DMARC Policy Decide What to Do with Every Email?
Your DMARC record policy gives you three options regarding what actions to take for an incoming email: none (nothing), quarantine, or reject. You have to define one of these actions in your DMARC record.
DMARC Policies:
- None: Do nothing with the email, as if DMARC was not installed. You should use this policy when you first implement DMARC in order to collect data about your email authentication status
- Quarantine: Accept the email but treat it very carefully. Quarantined emails may be considered suspicious or sent to the spam folder. In any case, it will not get to your recipient’s primary inbox
- Reject: An email will immediately get rejected when it fails authentication if you’re using the DMARC policy Reject
What is a DMARC Report?
DMARC reports notify you about important aspects of your sender’s domain including:
- Unauthorized Use of Your Domain
- Email Authentication
- Sending Volume and Frequency
- Potential Email Threats
There are two types of reports: aggregate and forensic. Let’s learn about what they are and how to analyze them to identify and fix email deliverability issues before they occur.
Aggregate Reports
Aggregate reports are XML files that contain information about all emails sent from your domain, regardless of whether they have failed DMARC authentication or not. They give you a high-level understanding of the performance of all messages sent from your domain through statistical data.
The only downside is that aggregate reports may be confusing to read, analyze, and store because it was created to be “machine-read.” That’s why we recommended using a DMARC analyzer to process the data.
Forensic Reports
Unlike aggregated reports, forensic reports are more specific. They show messages that failed DMARC authentication. They also provide details about subject lines, URLs included in the messages, failed SPF authentication, and DKIM signature problems.
Benefits of DMARC Email Security
If you haven’t deployed DMARC yet, now is a great time to start. Here is a quick list of five benefits you can get from having this email protocol in place:
1: Domain Visibility
DMARC shows you how your domain is being used across the Internet. The DMARC reporting mechanism will send aggregate reports about email messages that are being sent on behalf of your domain. These reports will reveal insights such as:
- Who is sending from your domains (both authorized and unauthorized IP addresses)
- How many emails are sent by each source
- What percentage of messages sent by legal sources are being properly authenticated
- Which sources are sending unauthenticated emails
- Which authentication method (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) is broken
These reports give you a complete overview of how your email domains are used and how you can better improve your email channel.
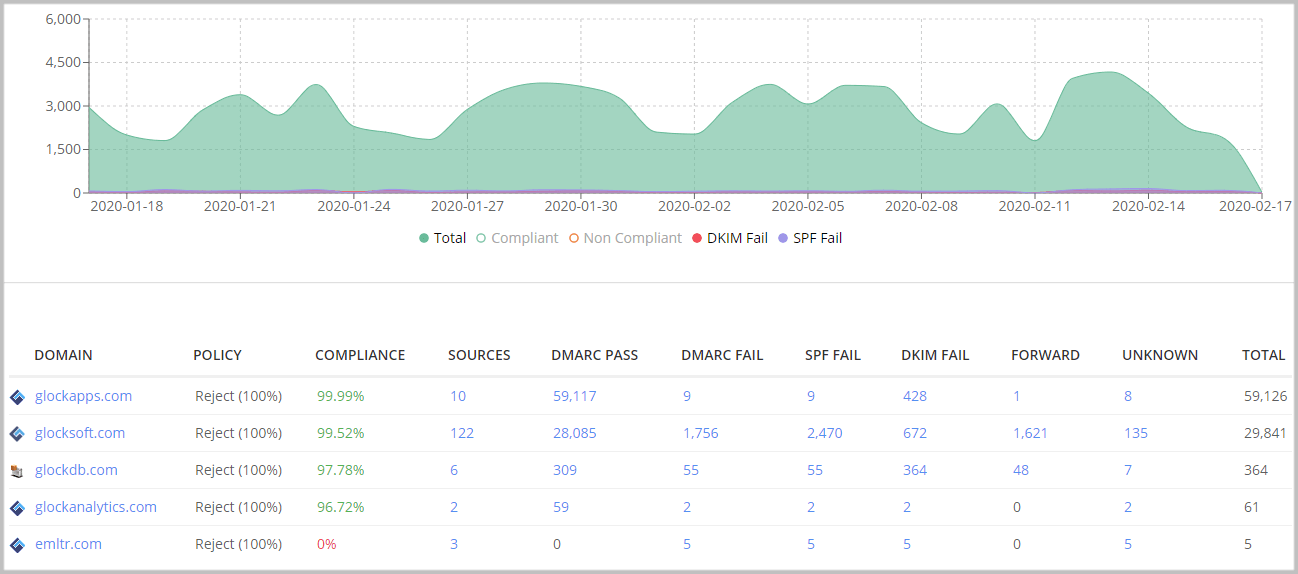
2: Control
Domain Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC record) gives you full control over the emails sent from your domains. If anyone starts abusing your domain, you will instantly see it in your report. Likewise, if any of your authorized IP addresses start sending unauthenticated emails, you’ll see it in your DMARC reports so you can correct any authentication issues.
The report shows you the volume of emails sent from your domains. So if you notice an unusual increase in sending volume, that may be a sign that your sender’s domain may have been spoofed. Check your report to see if it was sent from an authorized source or if it was from a spoofing attack.
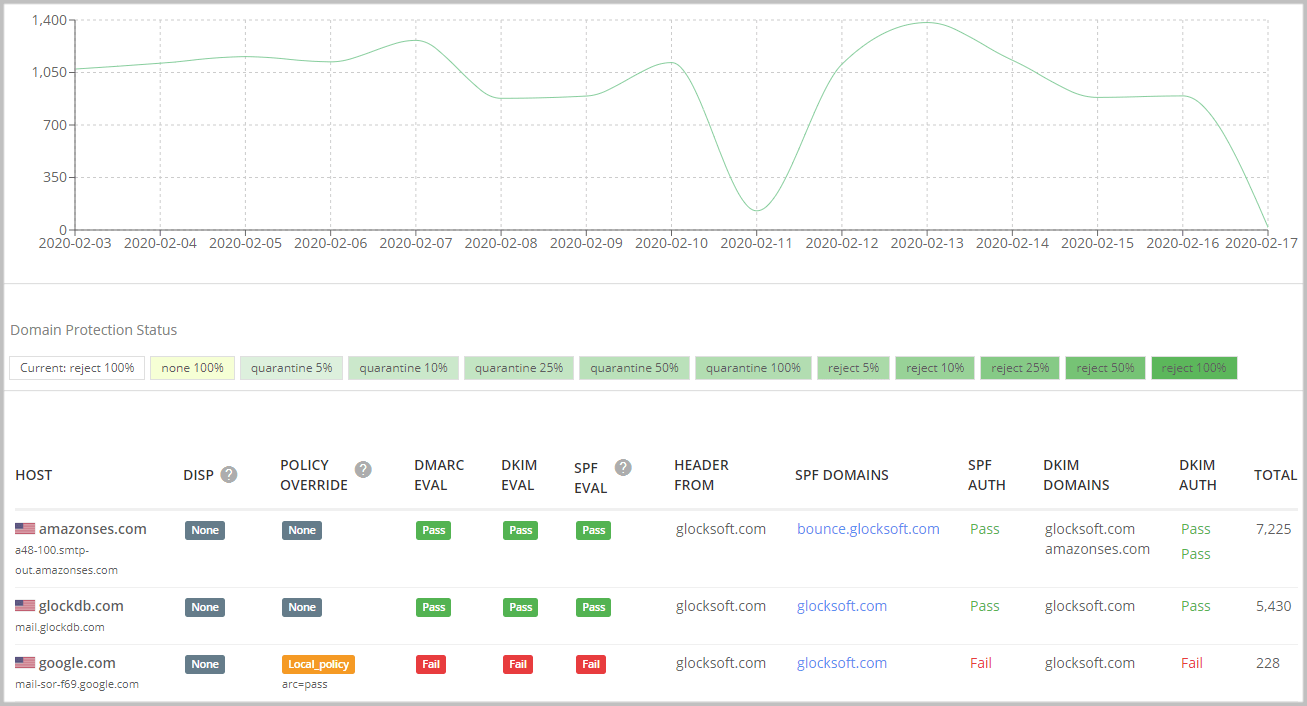
3: Security
Since the creation of email, users have had to deal with spam, phishing, and spoofed messages. Organizations had very little control over their domains to increase email security and prevent impersonation.
DMARC record solves this problem. You can instruct receiving mail servers what to do with a message that claims to be from your domain but isn’t authenticated.
You can also tell mailbox providers to reject any message sent from your domain that didn’t pass DMARC email authentication. This way, you protect your domain from being spoofed and protect your email receivers from spammers and scammers pretending to be you.
4: Brand Recognition
DMARC gives you access to the BIMI (or Brand Indicators for Message Identification) standard. BIMI has been adopted and supported by most email providers. Currently, Google, Yahoo!, Twilio SendGrid, Mailchimp, Valimail, Proofpoint, Validity, and Fastmail support BIMI.
BIMI provides email senders yet another way to stand out in their recipient’s Inbox by displaying their logo next to their message. This option gives your email instant brand recognition and credibility. You can use BIMI if you have strong email authentication and apply the “p=quarantine” or “p=reject” DMARC policy to unauthenticated messages.
5: Email Deliverability
DMARC reinforces SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). If your message passes DMARC domain alignment, it is always prioritized when determining email placement. Receiving mail servers have more trust in emails with strong authentication in place. So does DMARC improve email deliverability? Even though it’s not its primary goal – in many cases it does.
Moreover, if you implement DMARC enforcement with BIMI, you will have better email deliverability than other senders who don’t have it. Your email receivers will trust that a message comes from you and be more willing to open and respond to your email. Receiving mail servers see positive engagement as a good sign that your messages are wanted and deserve a place in your email receivers’ inbox.

Read: How You Can Leverage the DMARC Analytics to Fix Deliverability Issues
The good news is that, according to DMARC.org, the number of users who have implemented a valid DMARC record in their DNS records has increased to a total of 5.566 million in 2022 (according to global statistics).

Both SPF and DKIM protocols have their downsides, but DMARC gathers the results of their authentications to provide the best level of safety for your email channel.
Read more: How to Deploy DMARC Monitoring
DMARC Analyzer
How can you use DMARC to enhance your email channel after learning about its advantages?
When you run DMARC checks, they send DMARC reports as XML files to the address published in your rua tag. Some email senders may have a hard time deciphering and comprehending the data. Therefore, we strongly recommended you use third-party tools, like DMARC analyzers, that are specially created to receive, process, analyze and store your reports.
The GlockApps DMARC Analyzer tool runs your DMARC checks, receives reports, and presents the data in a human-friendly format. You can also quickly see your authorized and unauthorized mail streams sending DMARC compliant and non-compliant emails.
DMARC Record Analyzer
Learn More About DMARC Reporting:
DMARC Report Analyzer- Improve Email Deliverability
Why Every Business Needs DMARC
How to Protect Sender Domain with DMARC: Using DMARC Enforcement
DMARC Adoption: What’s the Problem?